
Population
New Zealand
Populaition Pyramid

New Zealand is a country that is in the third stage of the demographic transition model, suggesting that it has low birth rates along with low death rates, which basically means it substains the current population or very moderate population growth. This means that the country has established enough medical advancements making the population have no need to have more than a few kids (two). New Zealand is on it's way towards stage four in the demographic transition and you notice this by the birth rates declining towards the bottom of the pyramid than they were in previous years.
Cyprus
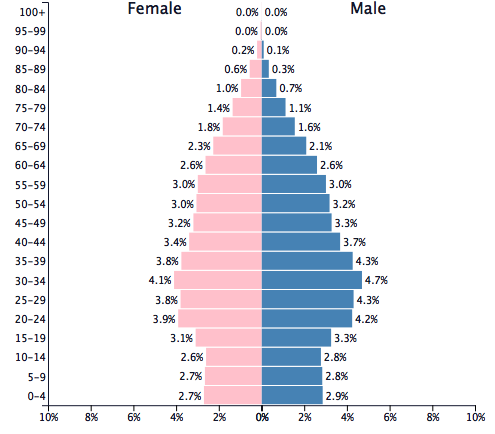
Population Pyramid
Cyprus is definitely a country that is rapidly expanding in population and overall through all categories of the demographic transition model. Although Cyprus has a huge population cluster towards the labor force ages, they are still fluctuating in the population throughout the younger ages. This is presented by the drop in birth rates, but towards the bottom the number of births appear to spike up again. This may be due to the new influence of diseases or infections, along with medical advances that allow lower infant mortality rates. In around 25 years or so the population of Cyprus will be more pushed towards the top making the dependency ratio extremely high while towards the middle and bottom the population will stay around the same. Eventually the population pyramid of Cyprus will look like a horizontal rectangle meaning the crude birth rates and crude death rates of the country will somewhat cancel each other out creating something called Zero Population Growth (ZPG) effect.
Population Statistics
New Zealand
Projected Population 2025- 5.16 million
Projected Population 2050- 5 million
Infant mortality rate- 4.2
Fertility rate- 2.05 births per woman
Urban population %- 86%
Urban population number- 30,000 approx.
CO2 emissions- 7.22 metric tons
Captia- Wellington
Population with access to clean water- 100%
Number of vehicles- 712/1000
Economically active male vs. female- 76%_62%
HIV infection rate- 0.000067%
Cyprus
Projected Population 2025- 1,261,000
Projected Population 2050- 1,401,000
Infant mortality rate- 8.1 deaths/1000 births
Fertility rate- 1.46 births
Urban population %- 67%
Urban population number- 786,108
CO2 emissions- 6.98 metric tons
Captia- Nicosia
Population with access to clean water- 100%
Number of vehicles- 675/1000
Economically active male vs. female- 71%_54%
HIV infection rate- 0.1%
Now Lets Compare...
Now that you have taken a look at the population pyramid for both Cyprus and New Zealand, along with their population statististic data, lets compare. New Zealand, is presented as having a pretty constant birth rate and population over the past 50 some years. Cyprus on the other hand, just started having a less fluctuating birth rate and population through the past 20 years. Therefore, you can tell that New Zealand and Cyrpus are quite similar in the development in their population. However, from the data presented above, New Zealand is on its way to the fourth stage of the demographic transition model, meaning that it will have extremely low birth and death rates with no population growth, even getting to a point where there is a decline in population. Cyrpus, is still on the verge of being in the third stage meaning that it has declining birth rates and population growth rates. To conclude, population is a key aspect in understanding and contrasting how developed a country is to one another.
Agriculture
New Zealand
Type of Agriculture Farming
The developed country, New Zealand, currently performs commercial agriculture. Commercial agriculture is normally found in More Developed Countries (MDC's), where the production of food is primarily for sale off the farm. New Zealand may have large commercial agriculture factors because they have more access to technology than Less Developed Countries (LDC's), which influences the amount of machines on each farm. The large surplus of New Zealand farms consists of vineyards which are prominent in the climate and geographical landscape present. Also New Zealand relies largely on their exports in the tradable economy, which makes them totally exposed to the international markets since subsidies were addressed into occurrence.
Main Types of Farming
In New Zealand, there are large amounts of livestock farming which primarily make up the agricultural exports of the country. New Zealand has suitable climate and landscapes that are prominent for dairy cattle, sheep, and the type of pastoral farming is beef cattle. For exporting, New Zealand ranks as the 8th largest dairy producer, and most is produced in the northern and southern areas of the country.
Impact of the Green Revolution
The Green revolution was a large increase in crop production in developing countries which was achieved by fertilizers, pesticides and several high yield crop varieties. This wouldn't have affected New Zealand as much as it did on other countries, which primarily consisted of intensive crop commercial agriculture. However, the Green Revolution was a major influence in the amount of crops and livestock being produced in New Zealand. The variety of high yield crop's (HYC) got larger and the amount of food regulating around the country grew. Since livestock is a major part of the New Zealand agriculture more food can be provided at cheaper prices forcing a larger profit sum. While the production of food and dairy from livestock would increase from the excess of food.
Percentage of Farmers in the Labor Force
In MDC's, the amount of farmers classified in the labor force is extremely less compared to those in LDC's. This is again due to the exposure of technology and machines, which increases the production rate and takes the place of many farmers. Therefore, in New Zealand the percent of farmers in the labor force is around 7%.
Future of Agriculture
The future of any agriculture in developed countries would be thought to improve with more innovations and advancements in technology. This can help to increase the importance and usefulness of machines on farms. In New Zealand, the dairy productivity has been on an incline for the past several years and is expected to keep rising. However, the landscape of New Zealand is getting disrupted as soil nutrients and other landscape factors are becoming exhausted. Therefore, the production of New Zealand agriculture is expected to go up as more profits are made, but at one point there needs to be a change because then the impact on the physical environment may be to severe to the country in the future.
Cyprus
Type of Agriculture Farming
The developing country, Cyprus, currently performs both Subsistence and Commercial Agriculture on somewhat large scales. Since Cyprus is still classified as a developing country, some residents who are farmers in the country still are involved in subsistence farming as technology and machine advancements may not be completely present in all farms. However, the agriculture sector of Cyprus actually is considered as the backbone of the economy in some ways because it has several large commercial agriculture farms that help with calculating exports and imports, impacting the development of the country.
Main Types of Farming
The primary types of farming located in the country of Cyprus are a complete variety of crops. The main crops produced in Cyprus are, wheat, barley, legumes, carrots, tomatoes, potatoes, along with fruit and other tree produced crops. This would be considered high yielding crops because they can produce a large amount of line grain crops in shorter amounts of time. Therefore, the agricultural portion of Cyprus is an important factor in the economy.
Impact of the Green Revolution
The Green Revolution was a large increase in crop production in developing countries which was achieved by fertilizers, pesticides and several high yield crop varieties. Since the major agriculture in Cyprus retains the crops the Green Revolution made a major impact on Cyprus. However, since it is still developing it may not have influenced every farm. But, in Cyprus the production rate at which crops are grown is higher, which makes the amount of profit sum increasing making the overall effect of agriculture in the country more substantially as more crops are produced.
Percentage of Farmers in the Labor Force
The amount of farmers in Cyprus is relatively low even though they are still considered a developing country, where typically everyone preforms some sort of agriculture. In Cyprus the entire economy is not as based off of agriculture as it is in New Zealand. However, due to the exposure of technology and machines, there are increases in the production rate and it takes place of many farmers. Cyprus has both large subsistence and commercial agriculture occurring making the amount of farmers in the labor force vary to some extent. The amount of farmers in the labor force of the country Cyprus is around 3.8%.
Future of Agriculture
The future of agriculture in the country of Cyprus seems to be prosperous. It is trying to advance in being more green and be more efficient through it's agriculture. Also, there are large increments of advancement in the agricultural and fishing industries throughout Cyprus. Attempting to be more cost-effective while the production of crops increases, makes the future of agriculture in Cyprus increasing in its impact on the overall economy.
